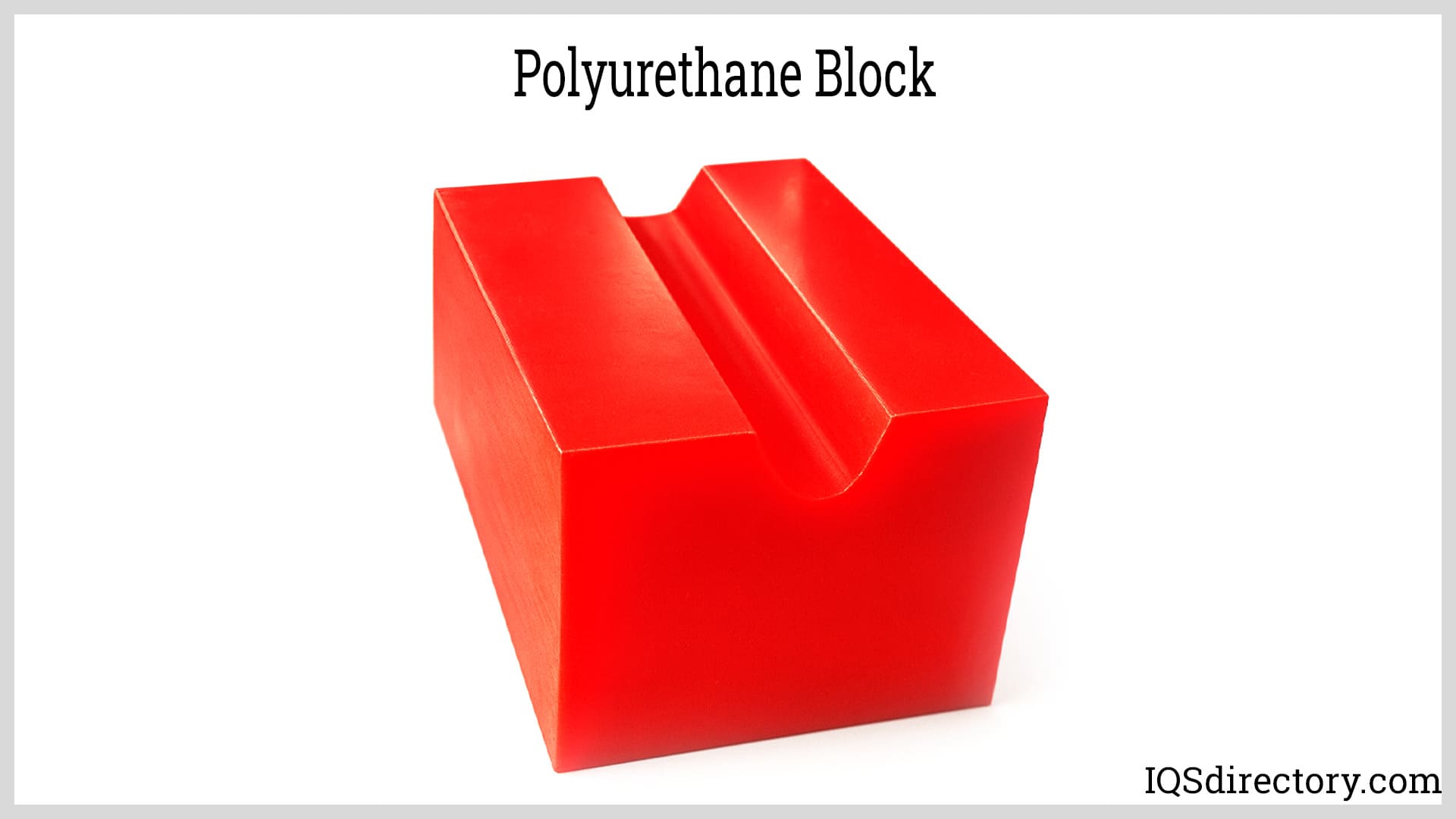
Polyurethane blocks are high-performance materials known for their durability, adaptability, and consistency across a wide range of industrial and manufacturing uses. Engineers, designers, and fabricators rely on them in applications that demand dependable mechanical strength, long service life, and predictable behavior under stress. Read More…
TPC, Inc. is a leader in the polyurethane molding industry. Our state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities focus on providing high-quality products, competitive pricing, and exceptional customer service. Our team of experts is dedicated to the production and innovation of our products. As a result, TPC, Inc.’s custom-fit solutions are perfected for customers of all industries.

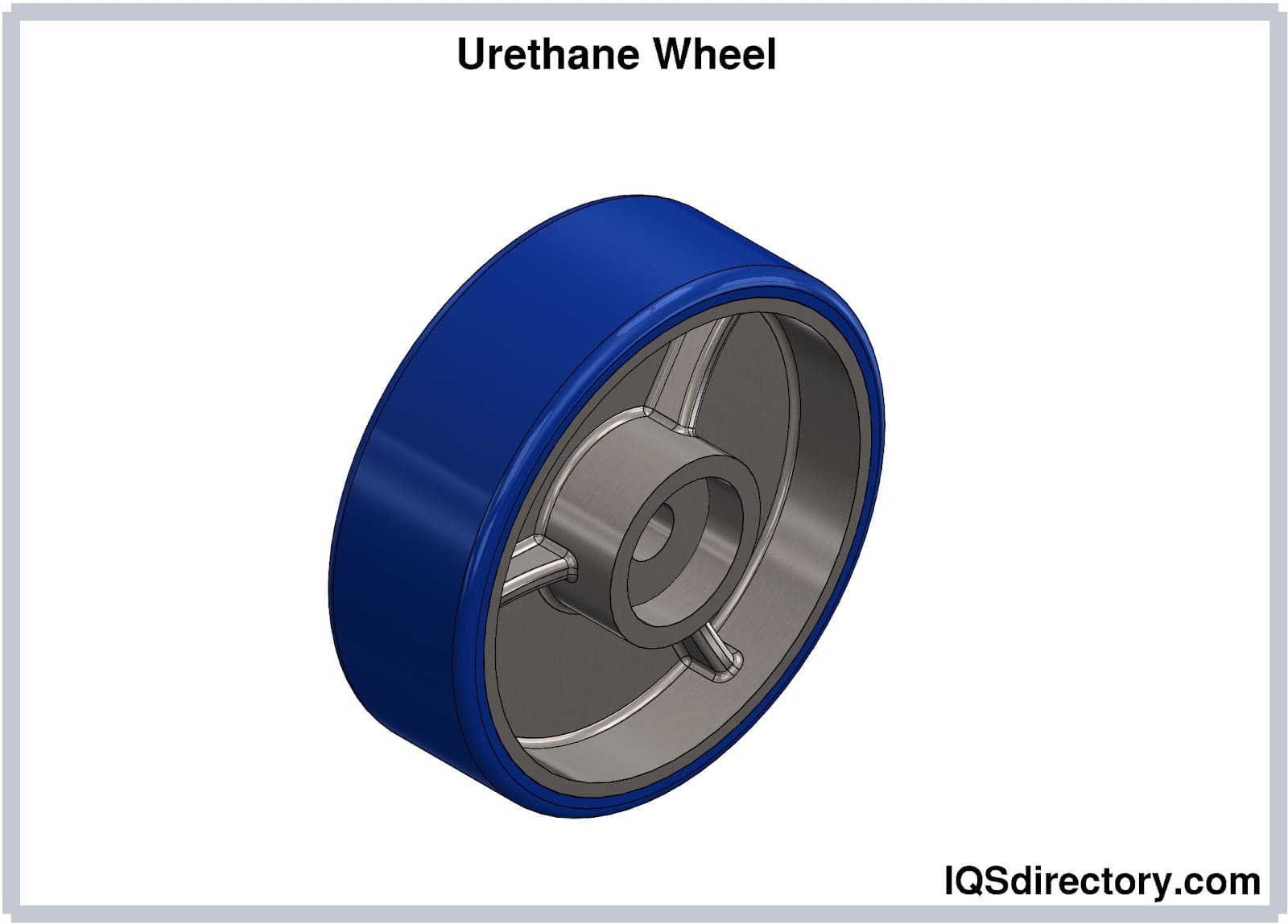
From concept, to production, to delivery, we have over 40 years experience with made-to-order cast urethane & cast polyurethane elastomer products. Weaver Industries offers urethane wheels, polyurethane molding, molded urethane, urethane sheets, & urethane/polyurethane manufacturing. Skilled at custom casting, discover the advantages of our urethane sheet and Action Mallet heads.

FallLine has been a manufacturer of custom polyurethane molding products for various industries since 1981. We offer a wide range of proven materials ranging from 40A - 80D, as well as the capability to formulate materials to meet specific needs.
Since 1979, Uniflex has been a leading manufacturer of urethane products. We provide high-quality urethane rollers and urethane castings, as well as urethane molded products available in an array of colors. Uniflex offers customized body blocks and engine components for the automotive industry. Our team is dedicated to advancing our company and raising industry standards.
More Polyurethane Block Companies
As engineered polymers increasingly replace wood, rubber, and even metal in many environments, polyurethane block stock has emerged as a go-to solution for impact resistance, wear resistance, dimensional accuracy, and load-bearing capability. These blocks are produced from advanced urethane elastomers or rigid foams and can be cast, molded, or machined to support both large-scale production and highly customized components.
Many buyers choose polyurethane blocks because they perform reliably under repeated vibration, continuous loading, exposure to chemicals, and challenging environmental conditions. That blend of toughness and versatility makes them well-suited for tooling, fixtures, seals, liners, bumpers, rollers, and structural parts. With a broad range of densities and hardness options available, polyurethane blocks allow manufacturers to refine prototypes, upgrade machinery, and improve product performance without the expense and lead times typically associated with metal fabrication or composite materials.
Performance Characteristics and Material Advantages
A major reason polyurethane blocks are in such high demand is their outstanding mechanical behavior. Polyurethane uniquely combines elasticity with rigidity, delivering properties that are difficult to achieve with other engineered materials. Its molecular structure provides excellent tear strength, compression resistance, and rebound resilience, helping blocks retain their shape under heavy loads and cyclical stress. Applications that rely on polyurethane often prioritize low compression set, strong abrasion resistance, and effective impact absorption because these traits directly influence equipment reliability and service life.
Chemical resistance is another key benefit. Polyurethane blocks perform well in environments where oils, fuels, solvents, and industrial lubricants are present. Compared with many rubbers and thermoplastics, polyurethane also maintains stability across a broader temperature range, making it suitable for operations involving thermal cycling or temperature extremes.
Noise and vibration control further enhance polyurethane’s value. When used as pads, isolators, bumpers, or machine components, polyurethane blocks absorb shock and dampen sound. In automated machinery, robotics, and conveyor systems, this vibration control improves precision, reduces wear, and contributes to safer, quieter workplaces.
Material Types and Formulation Options
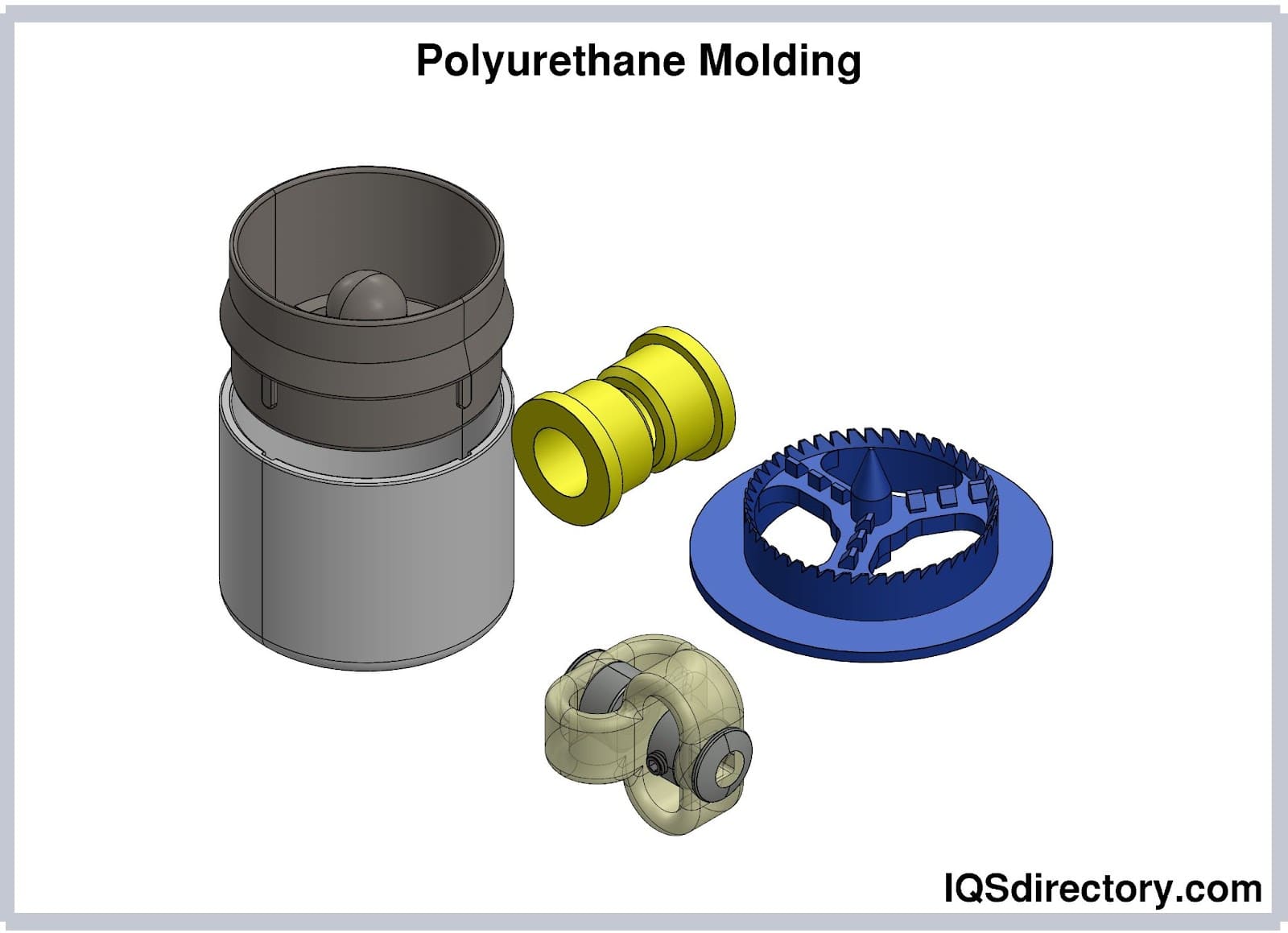
Polyurethane blocks are available in a wide variety of formulations designed to meet specific application requirements. Rigid polyurethane blocks are commonly selected for structural and load-bearing uses due to their dimensional stability and clean machinability. They are frequently used for pattern making, molds, and insulation applications where consistent density and predictable performance are essential.
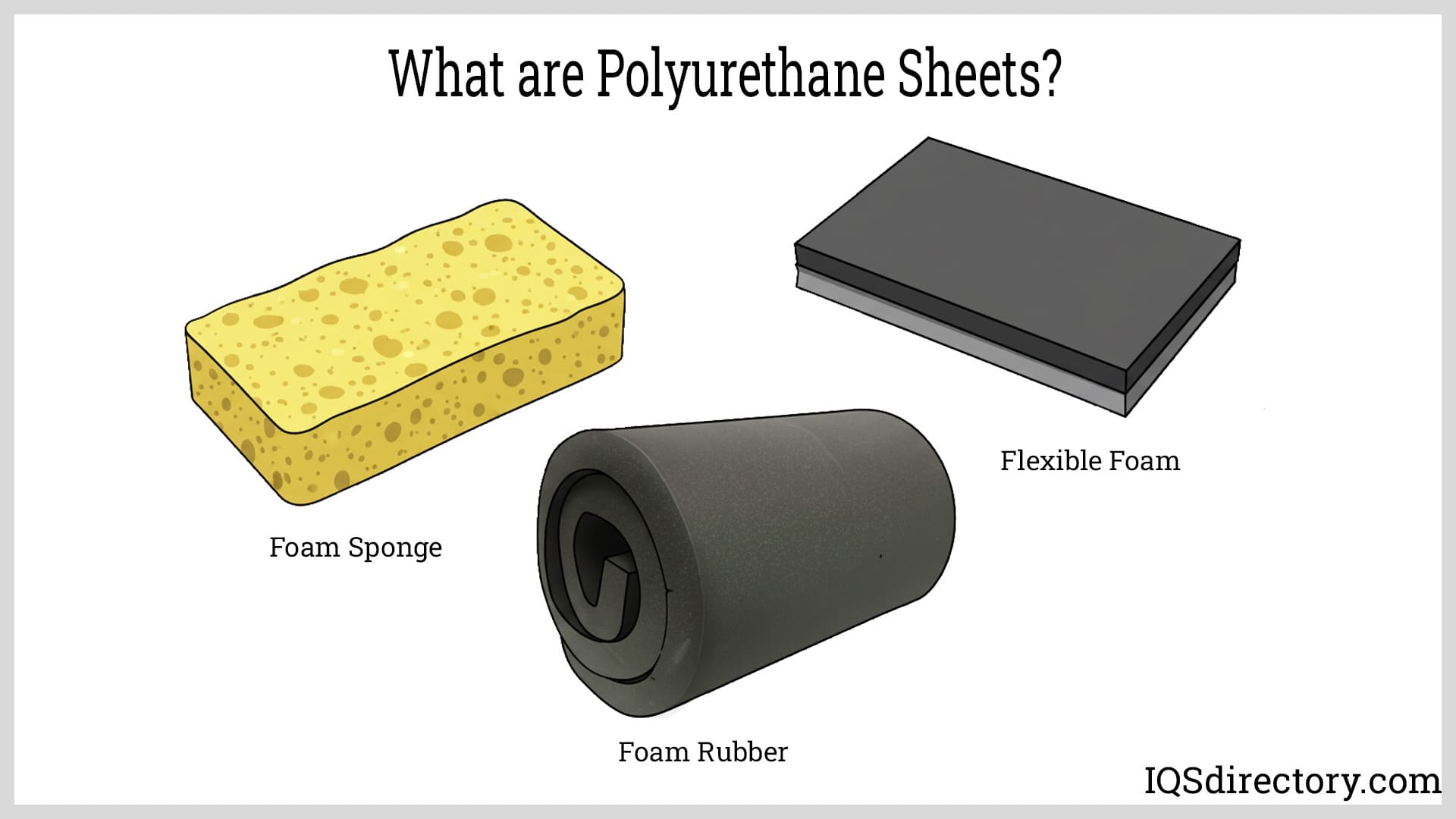
Elastomeric polyurethane blocks offer greater flexibility and dynamic load handling, making them ideal for industrial equipment and high-wear components. Their resistance to cracking and deformation under impact suits them for die-cutting pads, protective surfaces, and parts exposed to repeated stress.
Hardness selection plays a critical role in material performance. Softer grades excel in cushioning, sealing, and vibration isolation, while harder grades are better suited for rollers, spacers, wear strips, and precision fixtures. Custom urethane blends allow manufacturers to fine-tune tensile strength, elasticity, and elongation to meet exact performance goals.
Applications Across Industry
Because of their adaptability, polyurethane blocks are used throughout nearly every manufacturing sector. In machining and fabrication, they are commonly incorporated into fixtures, jigs, and work-holding components that stabilize parts during CNC operations without damaging sensitive surfaces. This makes them especially valuable when working with delicate metals, composites, or molded plastics.
In material handling and packaging operations, polyurethane blocks function as conveyor guides, impact bumpers, and protective pads that reduce equipment wear. Their resistance to cracking and chipping is particularly important in high-speed, high-volume conveyor systems.
Automotive, aerospace, and defense manufacturers use polyurethane block material for prototypes, model development, aerodynamic testing, and mold masters, taking advantage of urethane’s ability to be machined into intricate shapes while maintaining consistent strength. In construction and architectural projects, polyurethane blocks appear in insulation systems, formwork, decorative elements, and impact-resistant components that benefit from thermal stability and durability. Electronics and appliance manufacturers also rely on them for vibration-damping mounts, housings, and sound-control elements that enhance product performance.
Production and Machining Processes
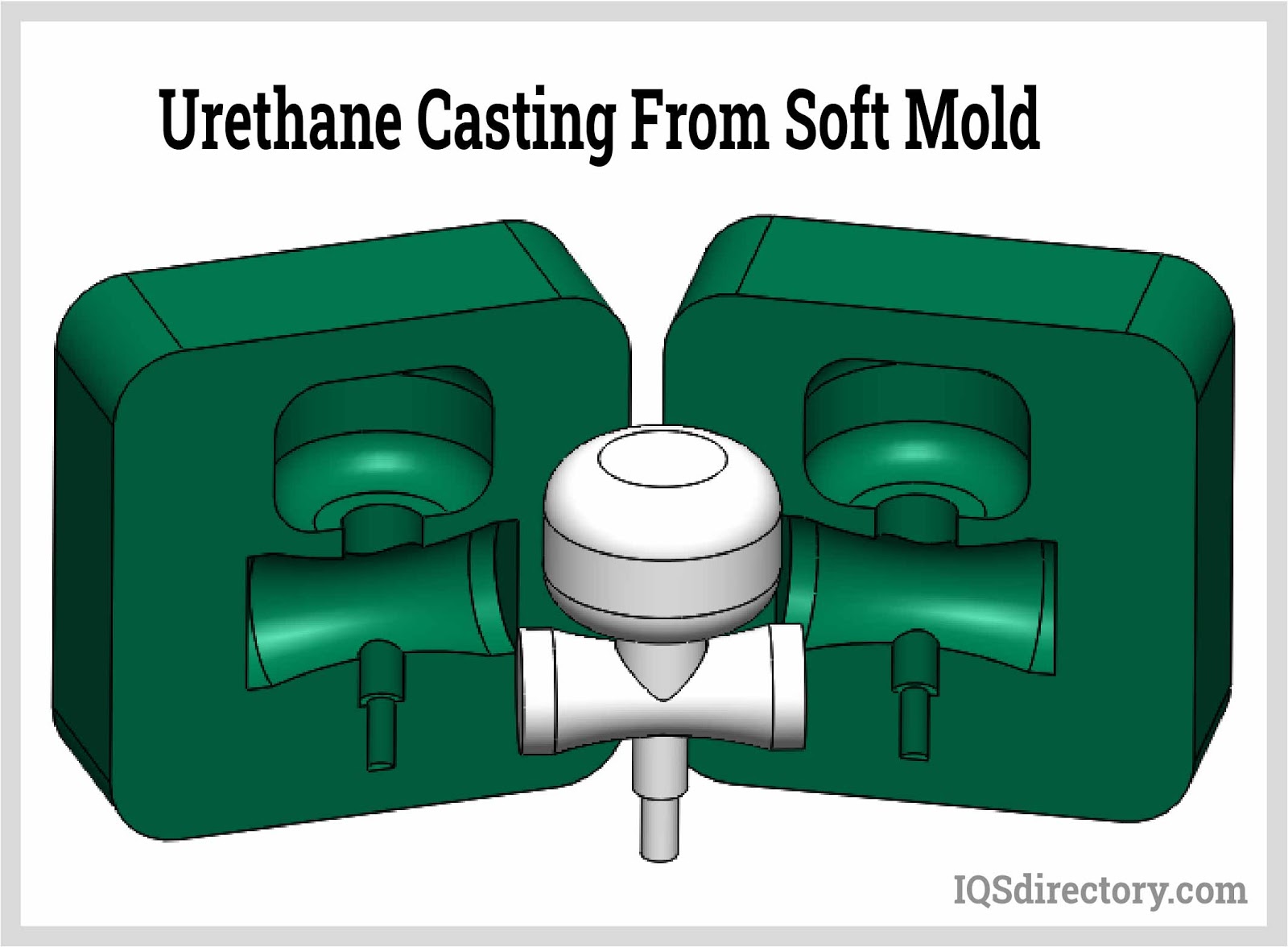
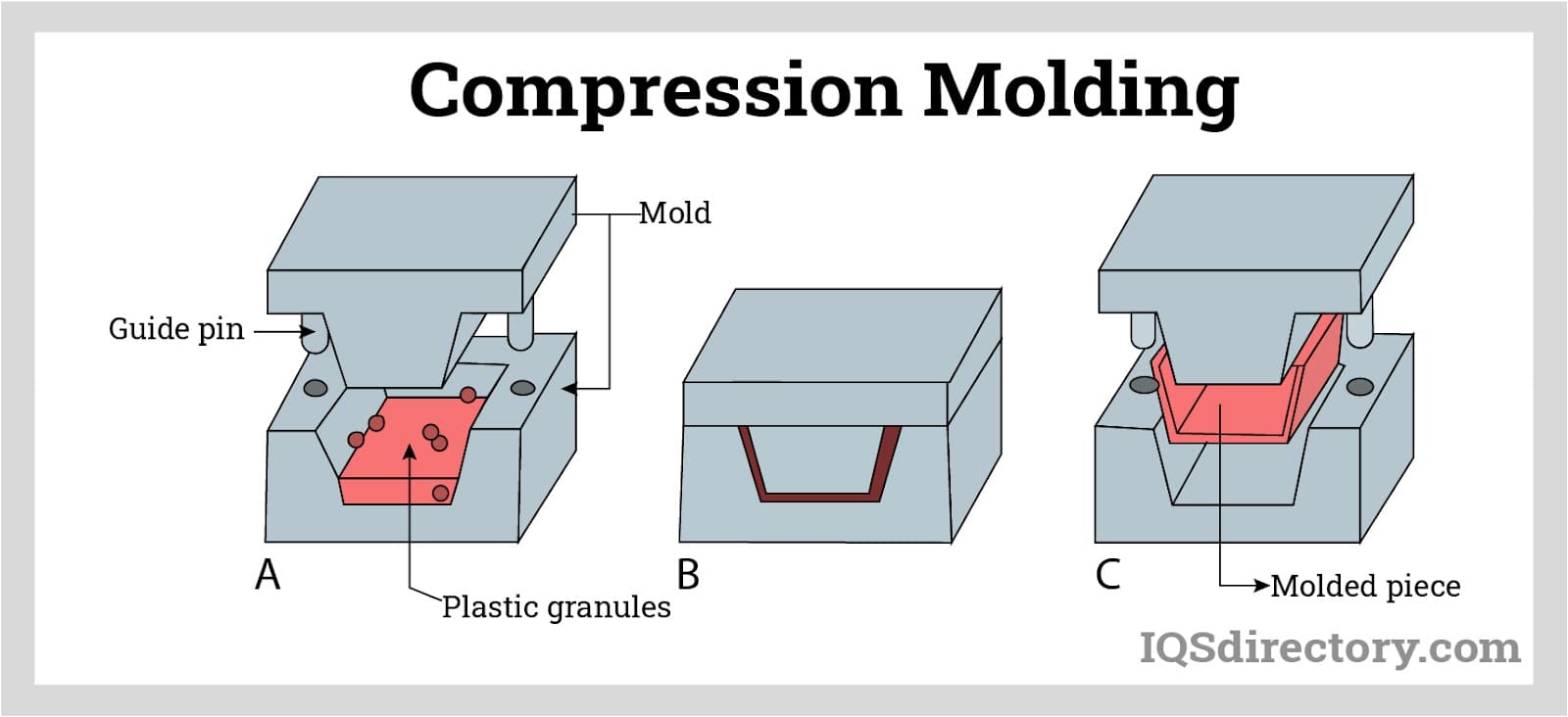
The manufacturing of polyurethane blocks begins with liquid urethane components that are carefully mixed under controlled conditions. By adjusting catalysts, additives, pigments, and curing parameters, producers achieve targeted hardness, density, and mechanical properties. The mixture is poured into molds where it cures or expands into block form.
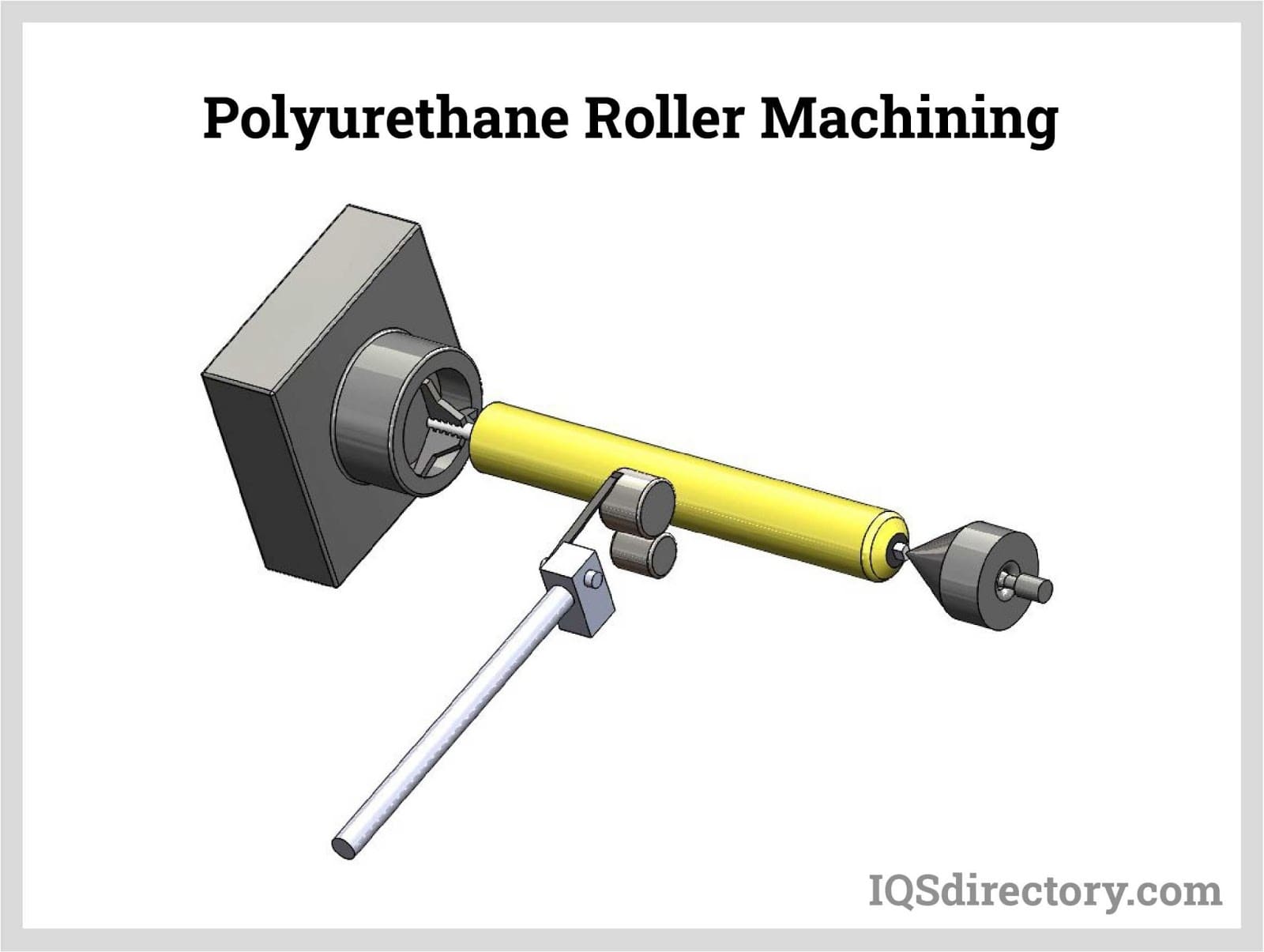
After curing, blocks may be trimmed, cut, or machined to meet precise dimensional requirements. Polyurethane machines similarly to softer metals or rigid plastics, allowing processes such as milling, drilling, turning, sanding, and waterjet cutting. This ease of machining supports rapid iteration in tooling and prototyping while keeping costs manageable. To ensure performance consistency, reputable suppliers test properties such as density, hardness, tensile strength, and compression behavior before releasing material to the market.
Value for Engineers and Purchasing Teams
Organizations select polyurethane blocks to extend component life, reduce maintenance demands, and improve overall efficiency. Parts made from polyurethane often outlast those made from rubber, wood, or lower-grade plastics, lowering replacement frequency and reducing total ownership costs.
Customization is another significant advantage. Suppliers can provide color-matched materials, flame-retardant options, FDA-compliant formulations, and anti-static or conductive grades to meet specialized requirements. Polyurethane also offers favorable strength-to-weight ratios compared to metals, enabling lighter components without sacrificing structural performance—an important consideration in systems where weight, inertia, or energy consumption matters.
Selecting the Right Polyurethane Block
Choosing the correct polyurethane block involves evaluating factors such as density and hardness, expected wear and abrasion, chemical exposure, temperature conditions, machining requirements, and production volume. Matching the formulation to real-world operating conditions helps prevent over-engineering while ensuring reliable long-term performance.
Ongoing Growth in Polyurethane Block Demand
As manufacturers continue to prioritize lightweight materials, rapid prototyping, flexible production methods, and durable polymer components, polyurethane blocks remain a practical and proven solution. Their ability to be precisely engineered, quickly machined, and reliably deployed in demanding environments supports innovation while controlling costs. For applications ranging from automation and equipment protection to structural support and advanced prototyping, polyurethane blocks continue to prove their value as essential materials in modern industry.






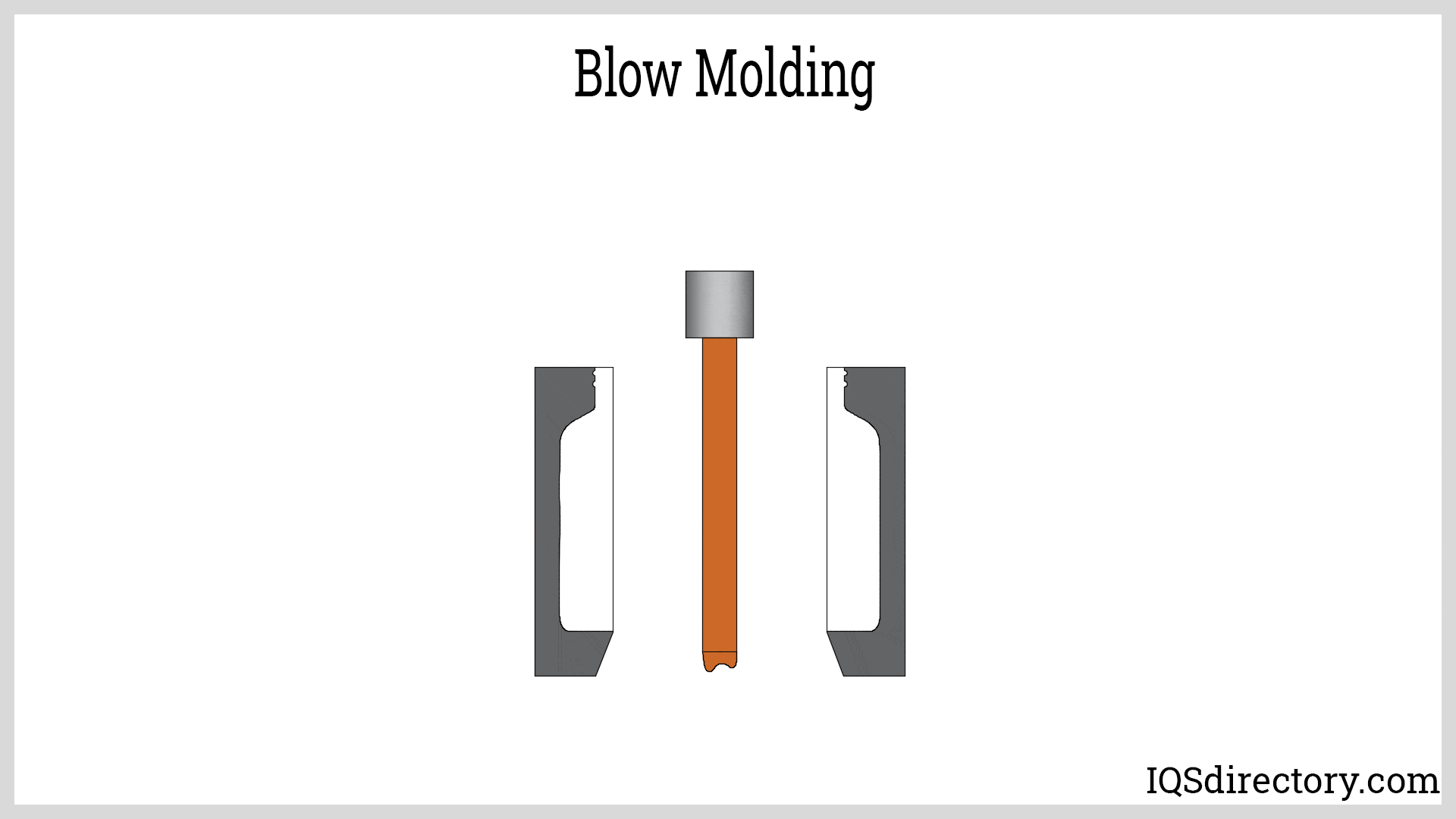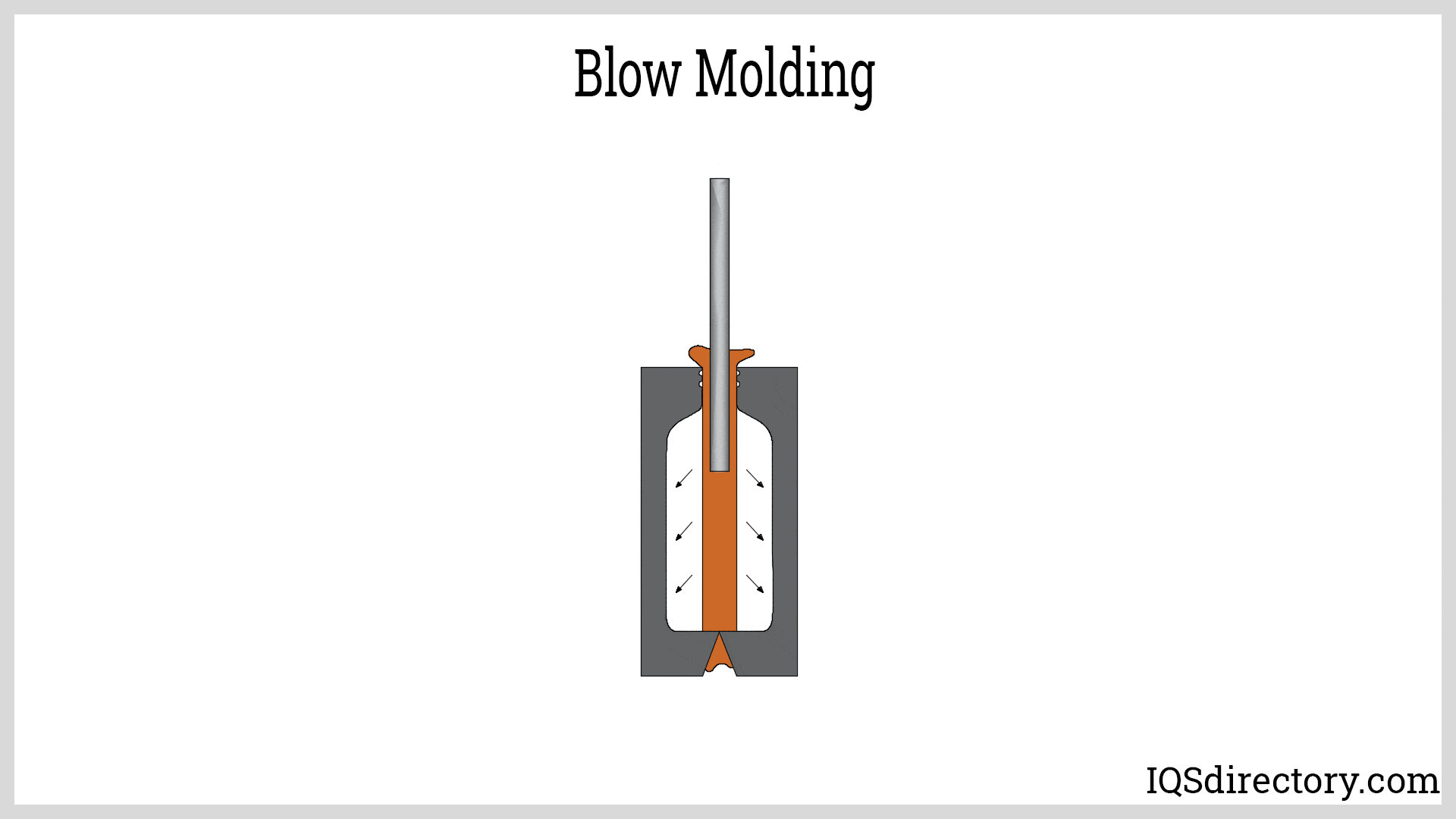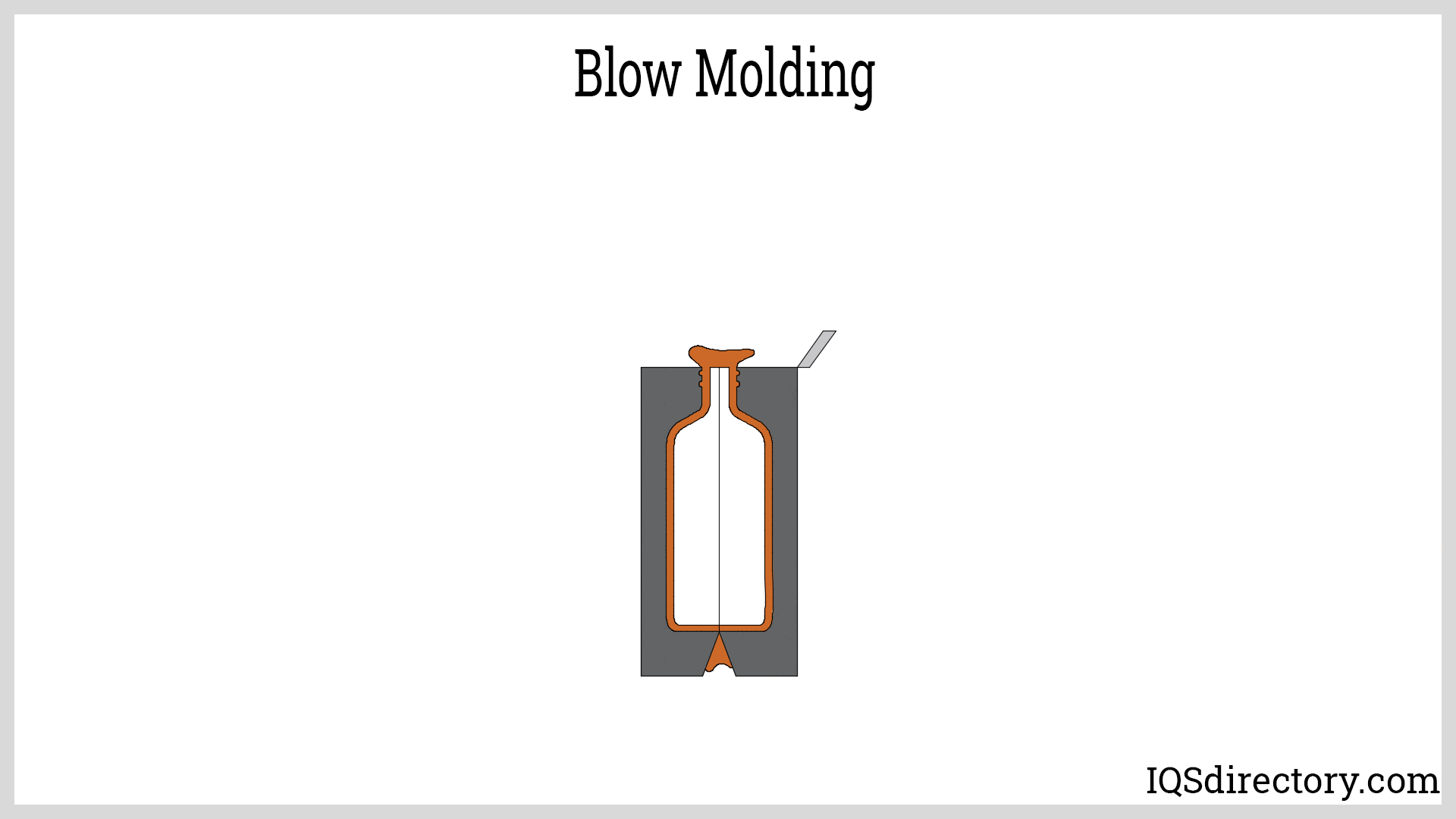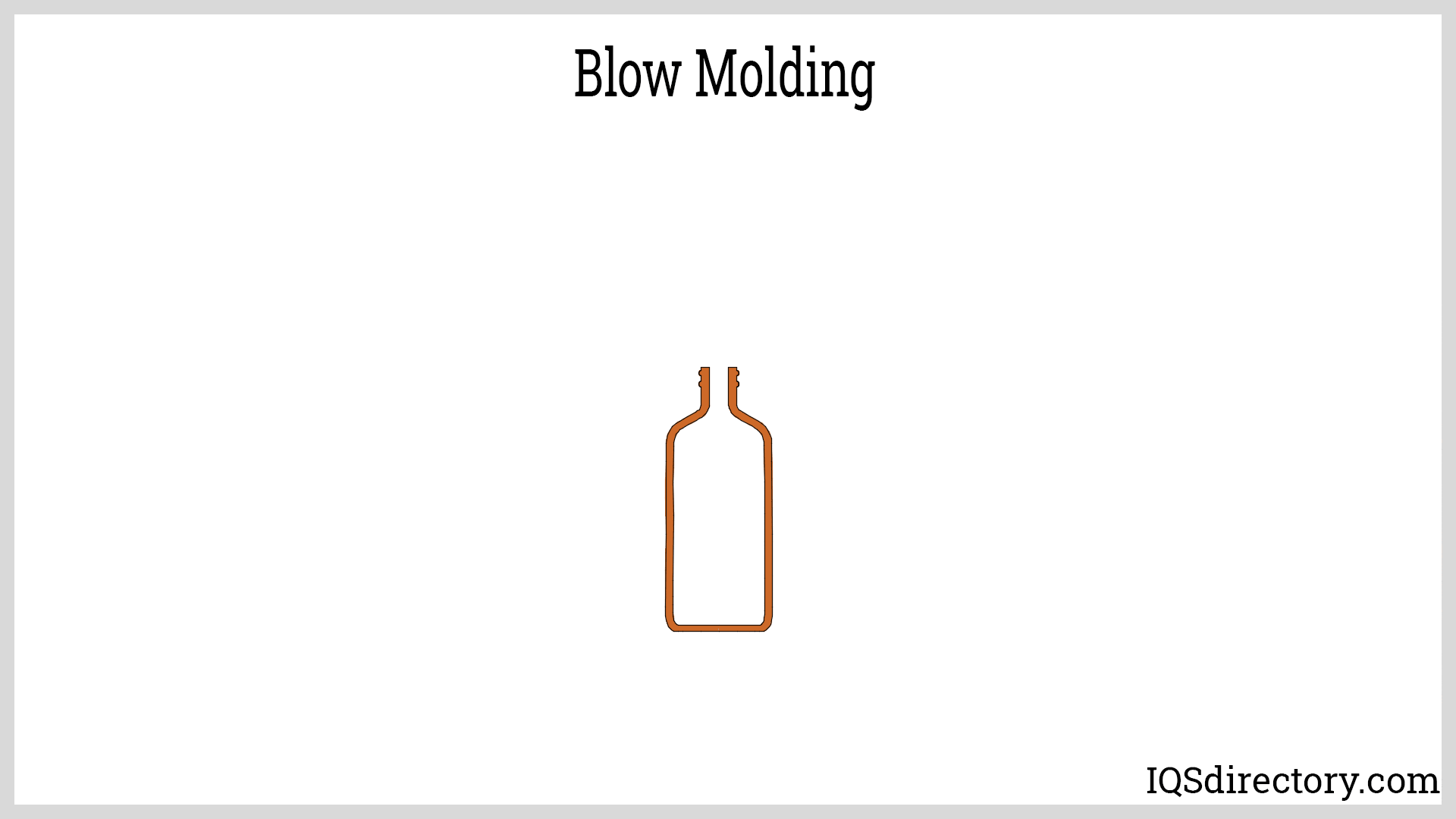



 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services